How Many Financed Properties Does FHA Allow?
The Federal Housing Administration (FHA) provides a range of loan options for homebuyers, including those looking to finance unique properties like barndominiums. However, there are specific restrictions and requirements that borrowers must meet. One common question is, “How many financed properties does FHA allow?” This article will address that question and delve into the FHA’s restrictions and requirements for building and financing a barndominium.
FHA Financing Limits on Multiple Properties
1. **Primary Residence Requirement**
**Single Property Focus:**
– FHA loans are designed primarily for owner-occupied properties, meaning the borrower must intend to live in the home as their primary residence. The FHA generally allows borrowers to have only one FHA-insured loan at a time.
2. **Exceptions to the One Loan Rule**
**Situational Allowances:**
– There are exceptions to the primary residence rule under specific circumstances. For example, if a borrower relocates for work and their current FHA-insured property is not within reasonable commuting distance, they may be allowed to obtain another FHA loan.
– Another exception includes a significant increase in family size, where the current FHA-insured home no longer meets the family’s needs.
3. **Non-Occupant Co-Borrower**
**Flexibility in Financing:**
– Non-occupant co-borrowers, such as parents helping their children buy a home, can be on the loan. However, the primary borrower must occupy the property as their primary residence.
FHA Requirements for Building and Financing a Barndominium
1. **Property Eligibility**
**Meeting FHA Standards:**
– For a barndominium to qualify for FHA financing, it must meet certain property standards. This includes being a single-family residence, adhering to local building codes, and passing an FHA appraisal.
– The property must have a permanent foundation, and the living area must be distinct and suitable for residential use.
2. **Construction Loans**
**FHA 203(k) Loan:**
– The FHA 203(k) loan program allows borrowers to finance both the purchase of a property and the cost of its rehabilitation through a single mortgage. This can be particularly useful for building a barndominium, as it covers construction costs.
– There are two types of 203(k) loans: Standard and Limited. The Standard 203(k) is for more extensive renovations, while the Limited 203(k) is for smaller projects not exceeding $35,000.
3. **Down Payment and Credit Score Requirements**
**Affordable Financing:**
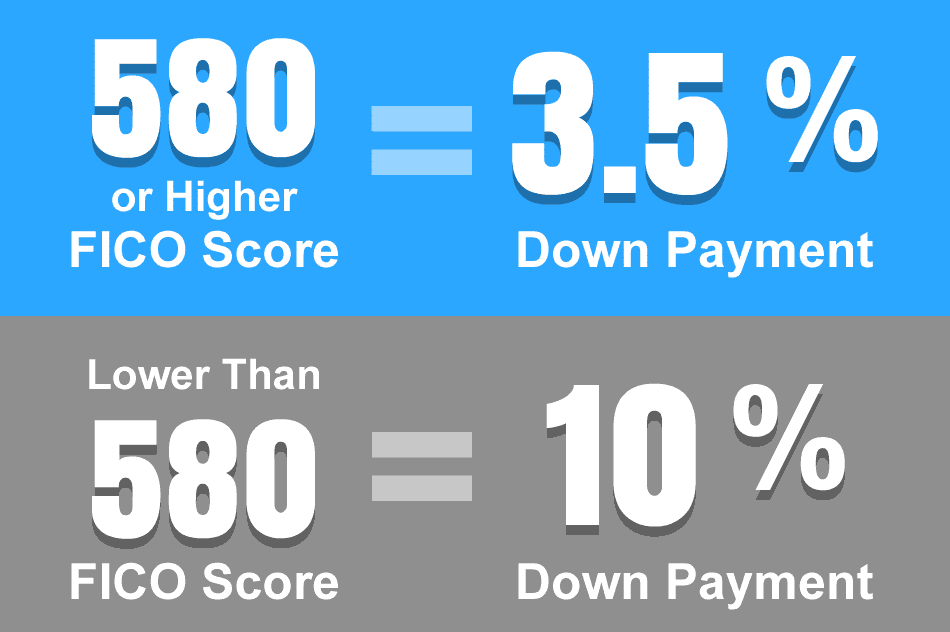
– FHA loans typically require a lower down payment than conventional loans, often as low as 3.5% of the purchase price.
– Borrowers need a minimum credit score of 580 to qualify for the 3.5% down payment option. Those with credit scores between 500 and 579 may still qualify, but they will need a higher down payment of 10%.
4. **Debt-to-Income Ratio**
**Ensuring Affordability:**
– The FHA imposes limits on the borrower’s debt-to-income (DTI) ratio to ensure they can afford the loan payments. Typically, the maximum DTI ratio allowed is 43%, although some lenders may allow higher ratios with compensating factors.
5. **Mortgage Insurance**
**FHA Insurance Premiums:**
– FHA loans require both an upfront mortgage insurance premium (UFMIP) and an annual mortgage insurance premium (MIP). The UFMIP is typically 1.75% of the loan amount, while the annual MIP varies based on the loan term, loan amount, and loan-to-value ratio.
6. **Appraisal Requirements**
**Property Valuation:**
– An FHA-approved appraiser must evaluate the barndominium to determine its market value and ensure it meets HUD’s minimum property standards. This includes an inspection of the property’s structure, roof, electrical systems, plumbing, and heating.
7. **Occupancy and Use**
**Primary Residence Clause:**
– As previously mentioned, the barndominium must be the borrower’s primary residence. FHA loans are not available for vacation homes or investment properties.
All-In-All
The FHA allows borrowers to have only one FHA-insured loan at a time, primarily intended for owner-occupied properties. Exceptions to this rule are limited and based on specific circumstances. For those looking to build and finance a barndominium, the FHA provides viable options through its loan programs, especially the 203(k) loan for construction and renovation. Meeting FHA requirements involves ensuring the property meets eligibility standards, securing a manageable down payment, adhering to DTI ratios, obtaining necessary insurance, and passing an FHA appraisal. Understanding these guidelines can help prospective barndominium owners navigate the financing process successfully.