The Role of Plastic Sheathing Under Concrete Slabs
In the world of construction, the integrity of a barndominium foundation is paramount. One common practice to ensure this integrity is the placement of plastic sheathing, or a vapor barrier, under concrete slabs. This layer of protection plays a crucial role in preserving the quality and durability of the foundation and, by extension, the entire structure. Here’s an in-depth look at why builders insist on this practice and how it benefits the barndominium over its lifespan.
Purpose of Plastic Sheathing Under Concrete Slabs
Moisture Control
The primary purpose of plastic sheathing under concrete slabs is to prevent moisture from the ground from penetrating the concrete. Soil naturally contains moisture, which can vary depending on weather conditions, soil composition, and groundwater levels. Concrete, being porous, can absorb this moisture if there isn’t a barrier in place. Over time, this moisture migration can lead to several problems, such as:
– **Structural Damage:** Moisture in the concrete can lead to expansion and contraction, which may cause cracking, heaving, or sinking.
– **Flooring Damage:** For buildings with sensitive flooring materials like hardwood or laminate, moisture rising from below can warp or buckle these surfaces.
– **Corrosion of Internal Reinforcements:** Steel reinforcement within concrete can rust when exposed to moisture, weakening the slab’s structural integrity.
– **Mold and Mildew Growth:** Excessive moisture is a breeding ground for mold and mildew, which can compromise indoor air quality and pose health risks.
Energy Efficiency
Another significant benefit of using plastic sheathing is improved energy efficiency. A dry foundation contributes to lower humidity levels inside the building, making air conditioning and heating systems operate more efficiently. This is because dry air is easier to cool and heat compared to moist air, leading to energy savings and a more comfortable indoor environment for your new Barndominium.
Pest Deterrence
Moist environments attract pests such as termites and carpenter ants, which can cause damage to wooden structures and other parts of the building. By preventing moisture from seeping into the concrete, plastic sheathing helps deter these pests from inhabiting and damaging the property.
Types of Plastic Sheathing
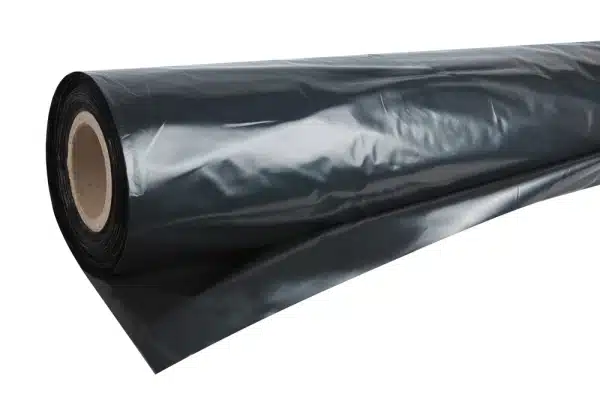
The most common type of plastic sheathing used in construction is polyethylene sheeting. This material is favored for its durability, resistance to punctures, and ability to block moisture effectively. It comes in various thicknesses, typically measured in mils (thousandths of an inch), with thicker options offering more robust barriers and longer lifespans.
When choosing a plastic vapor barrier for a slab foundation, the key is selecting a material that is durable, puncture-resistant, and impermeable to moisture. Here are the most common types of plastic used for this purpose, along with their characteristics:
Polyethylene Sheeting
Polyethylene sheeting is the most commonly used type of plastic for vapor barriers under concrete slabs due to its effectiveness in blocking moisture, affordability, and availability. Here are some specifics:
– **Thickness:** Polyethylene sheeting comes in various thicknesses, typically measured in mils (thousandths of an inch). For residential applications, a thickness of 6 mils is commonly used, but in areas with higher moisture levels or for commercial projects, thicker sheeting, such as 10 mils or 15 mils, might be preferred to ensure better durability and moisture resistance.
– **Durability:** Higher thickness generally correlates with greater resistance to punctures and tears during installation and over the lifespan of the building.
– **Color:** While often found in clear or black, choosing a black polyethylene sheet can help reduce light penetration, which may discourage the growth of mold or mildew under the slab.
Cross-laminated polyethylene
This type of sheeting is a more robust version of standard polyethylene. It involves multiple layers of polyethylene laminated together in a cross-grain pattern, enhancing its strength and resistance to tears and punctures. Cross-laminated polyethylene is particularly suitable for commercial projects or environments where soil conditions are aggressive.
Reinforced Polyethylene
Reinforced polyethylene includes a layer of reinforcing scrim between layers of standard polyethylene, which significantly increases its tear resistance and strength. This type is ideal for use in rough terrain or where the sheeting might be subjected to heavy stress during construction.
Vapor Barrier Installation Tips
When installing a vapor barrier under a slab, consider the following best practices to ensure effectiveness:
– **Overlap Seams:** Ensure that the seams between sheets of plastic overlap by at least 6 to 12 inches. Use a strong, waterproof tape to seal these seams securely.
– **Extend to Edges:** The vapor barrier should extend to the full width of the slab area and slightly up the sides of the foundation forms if possible.
– **Avoid Punctures:** Take care during the installation of rebar, wire mesh, and during the pouring of concrete to avoid puncturing the vapor barrier. Walk on boards rather than directly on the plastic when possible.
– **Repair Any Tears:** If the sheeting gets torn or punctured, repair it with the same waterproof tape used for the seams.
By choosing the appropriate type of plastic and following these installation guidelines, you can effectively protect your slab foundation from moisture ingress, thereby enhancing the durability and integrity of the entire structure.
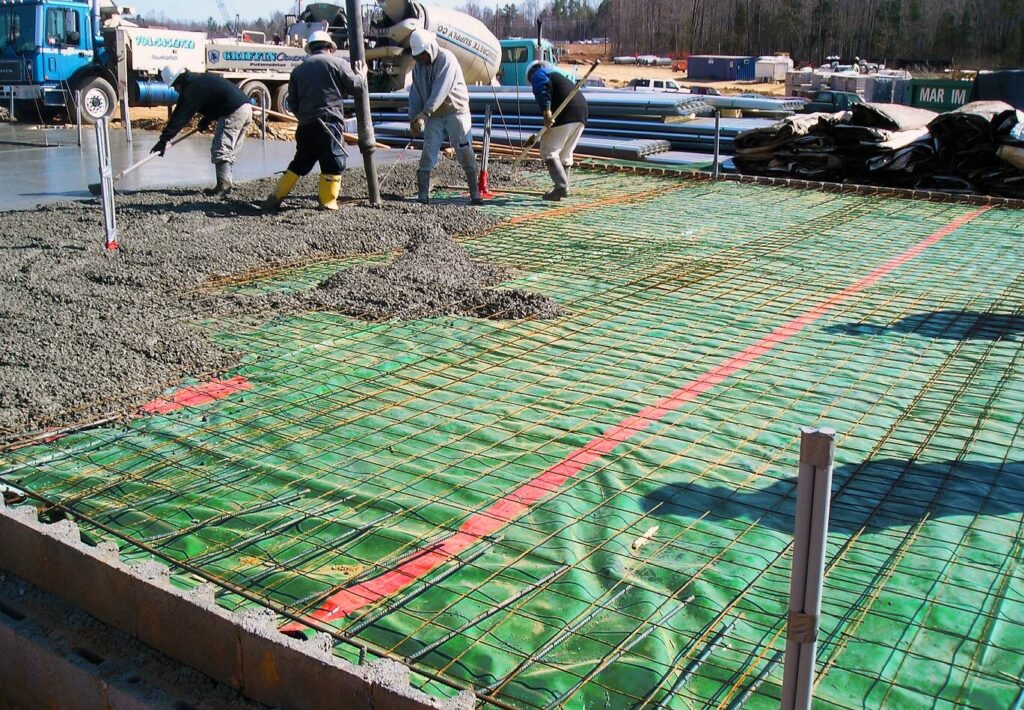
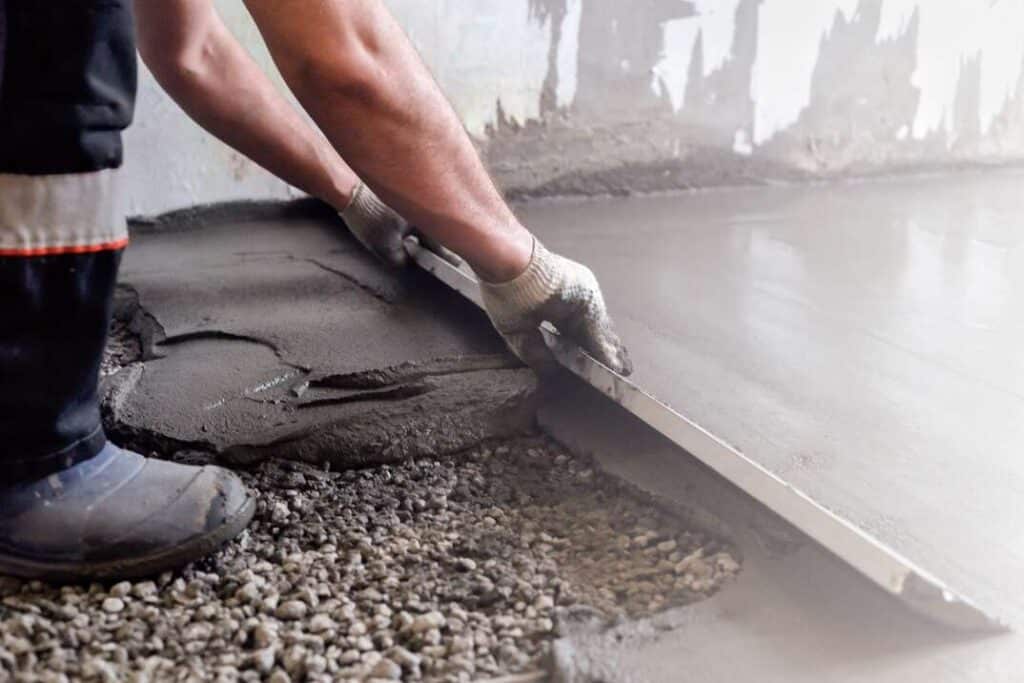
Installation Considerations
Proper installation of plastic sheathing is crucial for its effectiveness. The sheeting should cover the entire area under the slab and extend through the edges. Seams between sheets should be overlapped by at least 6 inches and sealed with tape designed for this purpose to prevent any gaps where moisture could enter.
Builders also need to ensure that the sheathing is not damaged during the concrete pour or by workers walking on it. Any punctures or tears can compromise its ability to block moisture and should be repaired before pouring the concrete.
The use of plastic sheathing under concrete slabs is a fundamental building practice designed to protect the foundation from moisture-related damage. Its benefits extend beyond simple moisture control, enhancing the barndominiums overall energy efficiency, structural integrity, and resistance to pests. By understanding and implementing proper installation techniques, builders ensure that their constructions stand the test of time, maintaining their stability, safety, and comfort for all occupants.