Will the California Wildfires Affect the Price of Lumber for 2025 and Beyond?
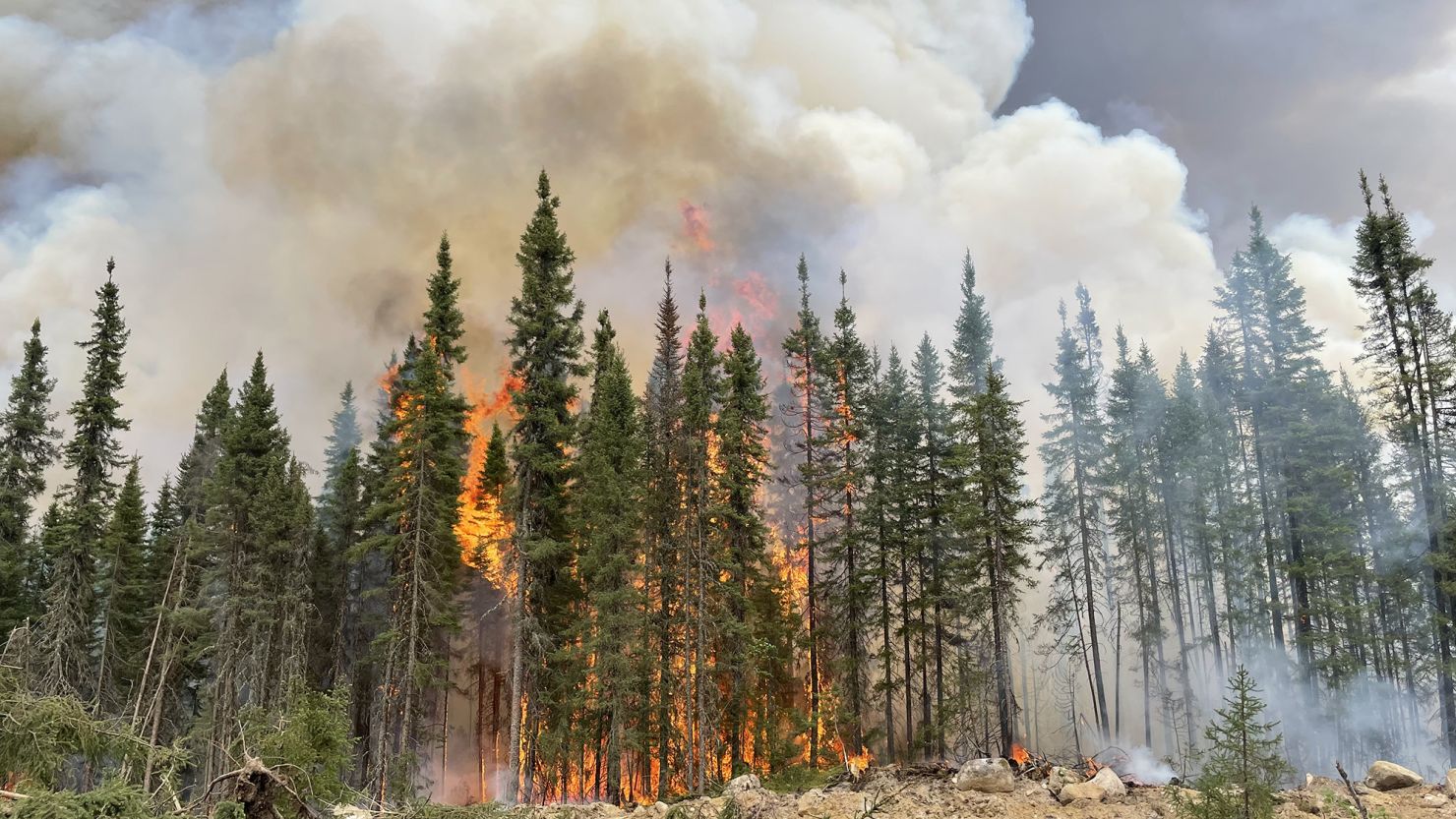
California’s devastating wildfires have far-reaching consequences beyond environmental and human impacts, rippling into industries like construction and agriculture. The lumber market, a cornerstone of the U.S. housing and building sector, is particularly vulnerable to these disruptions. This article explores how the California wildfires may influence lumber prices in 2025 and beyond, as well as the extent of California’s contribution to the nation’s lumber supply and the risks associated with wildfire exposure.
The Impact of California Wildfires on Lumber Prices
1. Reduction in Supply
California’s forest lands are a vital source of lumber, but wildfires have significantly reduced the availability of harvestable timber. When fires ravage forested areas, it takes decades for new trees to mature, leading to prolonged shortages. As a result, the decrease in supply can create upward pressure on lumber prices nationwide, as buyers scramble for alternative sources.

2. Increased Costs for Salvage and Reforestation
Recovering usable timber from fire-damaged forests is a costly and labor-intensive process. Salvage logging, which involves extracting burned or partially burned trees, often yields lower-quality wood and increases production costs. Moreover, reforestation efforts require substantial investment in planting, nurturing, and managing new forests, further driving up prices.
3. Supply Chain Disruptions
The infrastructure required to transport lumber from California’s forests to processing facilities and markets is often affected by wildfires. Road closures, power outages, and damage to processing plants can delay or halt operations, compounding supply shortages and escalating costs.
4. Increased Dependence on Imports
As California’s domestic supply becomes less reliable, the U.S. may increase its reliance on imported lumber from countries like Canada, Sweden, and Russia. While imports can stabilize supply, they often come with higher transportation costs and tariffs, further influencing domestic prices.
5. Impact on Housing and Construction Markets
Lumber prices directly affect construction costs, and as they rise, so does the cost of new home construction. This can lead to a slowdown in housing starts and renovations, particularly in regions where affordability is already stretched. Higher lumber prices may also encourage a shift toward alternative building materials like steel framing and engineered composites.
How Much of Our Lumber Comes from California?
California’s Contribution to U.S. Lumber Production
California produces approximately 10% of the U.S. lumber supply, making it a significant player in the industry. Its forests, including the Sierra Nevada and Coastal Ranges, provide softwood species such as Douglas fir, ponderosa pine, and redwood—highly valued for construction and specialty applications.
Lumber at Risk from Wildfires
The state’s susceptibility to wildfires poses a serious threat to its lumber resources. According to estimates, up to 60% of California’s commercially viable forestlands are located in areas at high risk of wildfires. Prolonged droughts, rising temperatures, and an accumulation of dry fuel exacerbate the frequency and intensity of fires, putting millions of acres at risk annually.
The Cascade Effect
California’s reduced output due to wildfires has a cascading effect on other lumber-producing states and regions. With less timber available from California, demand shifts to other domestic sources, such as the Pacific Northwest and the Southeastern U.S., straining their production capacities and pushing prices higher across the board.
Projections for Lumber Prices in 2025 and Beyond
Short-Term Volatility Lumber prices are expected to remain volatile in the short term due to uncertainty surrounding wildfire severity, salvage efforts, and supply chain resilience. External factors, such as economic conditions and housing market demand, will also play a role in price fluctuations.
- Long-Term Trends If wildfire activity continues at its current pace, lumber prices are likely to follow an upward trajectory in the long term. Increased investment in reforestation and fire prevention measures could mitigate some of these effects, but these efforts take years to yield results.
- Market Adaptation The industry may increasingly turn to innovative materials and practices to offset rising lumber costs. Engineered wood products, such as cross-laminated timber (CLT), and sustainable forest management practices could help stabilize supply and pricing.
Conclusion
California’s wildfires pose a significant challenge to the U.S. lumber market, with potential repercussions for supply, prices, and the broader construction industry. As approximately 10% of the nation’s lumber comes from California, the risks associated with wildfires are substantial, especially given that 60% of the state’s forestlands are in high-risk zones. While efforts to manage forests more sustainably and diversify supply sources could help mitigate these impacts, consumers and industries should prepare for higher lumber prices in 2025 and beyond.